Pancreatic trypsin enzymatic activity in broilers which intake royal palm nut meal
Main Article Content
Abstract
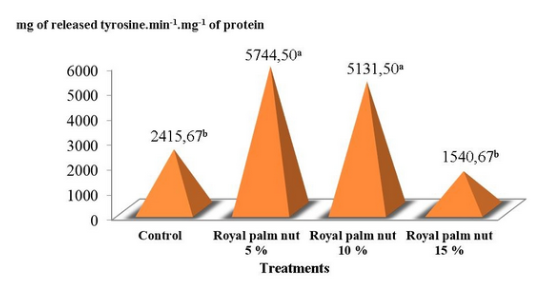
To study the pancreatic trypsin enzymatic activity in broilers which intake royal palm nut meal, a total of 40 animals (HE21) distributed in a completely random design were used. Four treatments were designed: control and inclusion of 5, 10 and 15 % royal palm nut meal. The animals were weighed and sacrificed at 42 days and the pancreas were extracted, they were weighed and expressed relative to live weight and the trypsin enzymatic activity was determined, which increased with the inclusion of 5 and 10 % compared to the control and 15 % (5744.50 and 5131.50 vs 2415.67 and 1540.67 mg of released tyrosine. min-1. mg-1 of protein, respectively). It is concluded that the inclusion of royal palm nut meal up to 10 % in broilers diets increase the pancreatic trypsin enzymatic activity to digest proteins in the gastrointestinal tract.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Those authors that have publications with this journal accept the following terms:
1. They will retain their copyright and guarantee the journal the right of first publication of their work, which will be simultaneously subject to the License Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) that allows third parties to share the work whenever its author is indicated and its first publication this journal. Under this license the author will be free of:
- Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
- Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material
- The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.
Under the following terms:
- Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- NonCommercial — You may not use the material for commercial purposes.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.
2. The authors may adopt other non-exclusive license agreements to distribute the published version of the work (e.g., deposit it in an institutional telematics file or publish it in a monographic volume) whenever the initial publication is indicated in this journal.
3. The authors are allowed and recommended disseminating their work through the Internet (e.g. in institutional telematics archives or on their website) before and during the submission process, which can produce interesting exchanges and increase the citations of the published work. (See the Effect of open access).
References
Bradford, M.M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72(1-2): 248-254, ISSN: 0003-2697. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3.
Di Rienzo, J.A., Casanoves, F., Balzarini, M.G., González, L., Tablada, M. & Robledo, C.W. 2012. InfoStat. Versión 2012, [Windows], Universidad Nacional de Córdoba, Argentina: Grupo InfoStat. Available: http://www.infostat.com.ar.
Duncan, D.B. 1955. Multiple range and multiple F tests. Biometrics, 11(1): 1-42, ISSN: 0006-341X. https://doi.org/10.2307/3001478.
Kuzmina, I.V., Tolpygo, S.M., Kotov, A.V., Shoibonov, B.B. & Zamolodchikova, T.S. 2024. Basal pancreatic secretion in a comparative aspect in poultry and rodents. Frontiers in Physiology, 15: 1340130, ISSN: 1664-042X. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2024.1340130.
León, M., Rueda, E., Castañeda, M., Méndez, A. & Michelangeli, C. 2007. Efecto de la concanavalina A sobre la actividad de las enzimas α-amilasa y tripsina en pollos de engorde. Revista Científica FCV-LUZ, 17(1): 83-88, ISSN: 2521-9715. https://produccioncientificaluz.org/index.php/cientifica/article/view/15261/15236.
Liu, S.Y., Selle, P.H., Raubenheimer, D., Gous, R.M., Chrystal, P.V., Cadogan, D.J., Simpson, S.J. & Cowieson, A.J. 2017. Growth performance, nutrient utilisation and carcass composition respond to dietary protein concentrations in broiler chickens but responses are modified by dietary lipid levels. British Journal of Nutrition, 118(4): 250-262, ISSN: 1475-2662. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114517002070.
Martínez-Pérez, M., Vives, Y. & Pérez-Acosta, O. 2021. Nutritional value of palm kernel meal, fruit of the royal palm tree (Roystonea regia), for feeding broilers. Cuban Journal of Agricultural Science, 55(3): 305-313, ISSN: 2079-3480. https://www.cjascience.com/index.php/CJAS/article/view/1026/1339.
Singh, A.K. & Kim, W.K. 2021. Effects of dietary fiber on nutrients utilization and gut health of poultry: A review of challenges and opportunities. Animals, 11(1): 1-18, ISSN: 2076-2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010181.
Vertiprakhov, V.G., Grozina, A.A., Fisinin, V.I. 2020. The exocrine pancreatic function in chicken (Gallus gallus L.) fed diets supplemented with different vegetable oils. Agricultural Biology, 55(4): 726-737, ISSN: 2412-0324. https://doi.org/10.15389/agrobiology.2020.4.726eng.
Vertiprakhov, V.G., Trukhachev, V.I. & Ovchinnikova, N.V. 2023. Trypsin cycling in poultry is associated with metabolic regulation. Frontiers in Physiology, 14: 1226546, ISSN: 1664-042X. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2023.1226546.
Vives, Y., Martínez-Pérez, M., Alberto, M. & Hernández, Y. 2020. Pancreatic lipase enzymatic activity in broilers fed with Roystonea regia fruit meal included in the ration. Technical note. Cuban Journal of Agricultural Science, 54(1): 101-105, ISSN: 2079-3480. https://www.cjascience.com/index.php/CJAS/article/view/940/1021.
Vives, Y., Martínez-Pérez, M. & Hernández, Y. 2021. Morphometric indicators of broilers fed Roystonea regia fruit meal in the ration. Technical note. Cuban Journal of Agricultural Science, 55(2): 181-184, ISSN: 2079-3480. http://www.cjascience.com/index.php/CJAS/article/view/1019/1327.